VaadinNotes » History » Revision 115
« Previous |
Revision 115/125
(diff)
| Next »
Andreas Kohlbecker, 07/03/2017 05:36 PM
Vaadin Development Resources¶
See also the VaadinEditorDevelopersGuide
Vaadin is an open source Web application framework for rich Internet applications. In contrast to JavaScript libraries and browser-plugin based solutions, it features a server-side architecture, which means that the majority of the logic runs on the servers. Ajax technology is used at the browser-side to ensure a rich and interactive user experience. On the client-side Vaadin is built on top of and can be extended with Google Web Toolkit.
This page holds information and resources for developing with the GWT-based Vaadin-Framework. For general information to this framework see: https://vaadin.com/faq
(quoted from Wikipedia:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vaadin, the free encyclopedia)
- Table of contents
- Vaadin Development Resources
- General Structure of Vaadin
- Development Environment Setup
- cdm-vaadin project
- Servlet Deployment Configuration
- Authentication with Vaadin & Spring Security
- Vaadin run modes
- Vaadin AddOn's
- Design patterns
- CDM Library Specific Development
- References and other goodies
- Performance
- Miscellaneous Notes
- Conventions & Policies
- Vaadin Security
General Structure of Vaadin¶
The Vaadin architecture can be split very roughly into client and server side.
The server side holds all the business logic and services as well as the standard java vaadin components, which will be translated into JavaScript later on.
The client side incorporates the GWT-part as well as client side specific JavaScript code, to do some more dynamic manipulation on the browser side.
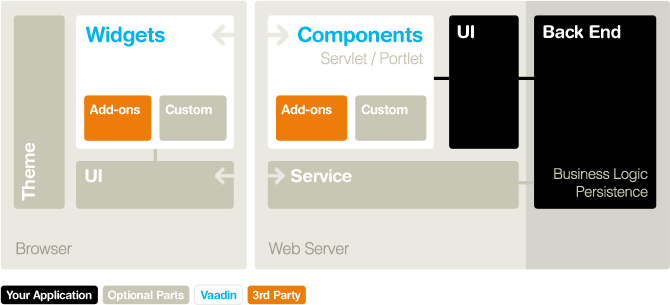
All Vaadin Components are written in plain Java. There is no need to program in JavaScript or even HTML. This all will be compiled by the framework. See the next section for supported browsers.
Browser compatibility¶
Vaadin 7 supports the following browsers:
- Android 2.3 or newer
- Google Chrome 23 or newer
- Internet Explorer 8 or newer
- iOS 5,6,7 or newer
- Mozilla Firefox 17 or newer
- Opera 12 or newer
- Safari 6 or newer
NOTE: From release 7.2+ all permutations have been merged into a single one - refer #13274
Development Environment Setup¶
please refer to VaadinEditorDevelopersGuide
cdm-vaadin project¶
The cdm-vaadin project is a stand-alone war Eclipse / Maven project, which includes cdmlib dependencies allowing it to function as a full-fledged web application. This allows for testing the vaadin framework with the cdmlib. This project itself is not a target for deployment as a webapp, but is integrated into the cdmlib-remote-webapp project as described below.
For more details on the Vaadin integration in Maven please see https://vaadin.com/wiki/-/wiki/Main/Creating+a+Maven+project
This maven plugin is base on gwt-maven-plugin. Therefore the Goals and Parameters Reference of this plugin also accounts to the vaadin plugin.
Vaadin specific maven goals include,
vaadin:clean vaadin:resources vaadin:update-theme vaadin:update-widgetset vaadin:compile-theme vaadin:compile
cdm-vaadin project integration with the cdmlib-remote-webapp¶
To Be Done
Servlet Deployment Configuration¶
With Servlet 3.0+ all configuration other wise declared in web.xml can now be declared using annotations in specfic Java classes. The servlet deployment configuration for the project consists of,
- Web Application Initializer : consists currently of two main parts, both of which are declared in the 'eu.etaxonomy.cdm.vaadin.CdmAppInitializer' class.
- ContextLoaderListener, a servlet context listener that associates a Spring application context with your servlet context and makes it accessible to other Spring classes. Typically this is defined via an applicationContext.xml file that sits in WEB-INF.
- DispatcherServlet, a regular Java servlet that Spring provides. Each such servlet has its own Spring application context - distinct from, though a "child" of, the one mentioned above associated with the ContextLoaderListener. If your servlet is named foobar then the default XML file name is foobar-servlet.xml.
- Servlet Mapping : primarily connects a Vaadin UI class to a VaadinServlet class, with 'init-param' style annotations. Any of the UI classes in the project can be looked up for examples of this configuration.
NOTE: The 'Web Application Initializer' part of the configuration does not yet work for the moment (refer #4527) and is set for now in the web.xml.
Authentication with Vaadin & Spring Security¶
The vaadin-spring addon provides build in access control in the SpringViewProvider: View-based security can be provided by creating a Spring bean that implements the interface com.vaadin.spring.access.ViewAccessControl (for view bean name and annotation based security) or com.vaadin.spring.access.ViewInstanceAccessControl (if view instance specific contextual data is needed). It is also possible to set an 'Access Denied' view by using setAccessDeniedViewClass(Class).
IMPORTANT NOTES:
- CSRF: Both Vaadin and Spring Security have built-in protection for Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF). You have to disable one of them, otherwise your application will not work properly.
Further interesting references:
- https://vaadin.com/blog/-/blogs/filter-based-spring-security-in-vaadin-applications
- https://vaadin.com/blog/-/blogs/a-hybrid-approach-to-spring-security-in-vaadin-applications*
Vaadin run modes¶
Production Mode¶
Configured in /src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/web.xml and also via the @VaadinServletConfiguration(productionMode = true, ...) annotation for the classes in the eu.etaxonomy.cdm.vaadin.ui package. The annotation based configuration does not seem to have an effect though.
SuperDev Mode¶
see VaadinEditorDevelopersGuide for details
Vaadin AddOn's¶
The official Vaadin website hosts a directory of all available AddOn's http://vaadin.com/directory.
In order to add an extension to your project add the maven dependencies to your pom file.
Vaadin Spring¶
The Vaadin Spring integration library helps you build amazing Vaadin based user interfaces on top of your high quality Spring based enterprise backend. Your UI classes become Spring managed beans, allowing you to autowire Spring based services directly into your UI code.
See also #5285.
Links:
- Vaadin Spring API
- Vaadin Spring Tutorial
- https://vaadin.com/wiki/-/wiki/Main/Spring%20Integration (on Vaadin 6)
- https://vaadin.com/wiki/-/wiki/Main/Vaadin+Spring
The features of Vaadin Spring include:
- First class support for Spring Boot
- Vaadin UI, View and component classes can be Spring managed beans and utilise the IoC container provided by Spring core
- @SpringUI annotated classes are automatically published, no need to manually introduce a servlet
- Vaadin Navigator support for View classes annotated with @SpringView
- Scopes for Vaadin UIs and Views
- Using the @Autowired annotation in Vaadin UI code
- Push support
Note: THE BOOK OF VAADIN (2016-04-19) IS OUTDATED REGARDING VAADIN-SPRING!
Addon - Vaadin4Spring Event Bus¶
https://github.com/peholmst/vaadin4spring/tree/master/addons/eventbus
This event bus infrastructure complements the org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher in the following ways:
- Events propagate from parent buses to children
- Events are scoped
There are four event scopes, and therefore four event bus types (each with their own sub interface):
- EventScope.APPLICATION events are published to the entire application.
- EventScope.SESSION events are published to the current session.
- EventScope.UI events are published to the current UI.
- EventScope.VIEW events are published to the current view.
The event buses are chained in the following way:
- Application events are propagated to the session event bus.
- Session events are propagated to the UI event bus.
- UI events are propagated to the view event bus.
Viritin¶
Viritin is a server side enhancement library for Vaadin. It fixes some bad defaults in the core framework and provides more fluent and intelligent API for existing components. It also provides several major enhancements to databinding and provides completely new components made with server side composition (no widgetset is needed).
For the cdm-vaadin project the most important feature of viritin is the support for lazy data binding in List fields like for example the LazyCobmobox. The containers being used in Viritin are capable of using service layer pager methods to fetch items only when needed. See the Viritin blog - Connecting large amounts of data to UI. For a example implementation in the cdm-vaadin project please refer to src/main/java/eu/etaxonomy/vaadin/component/ToOneRelatedEntityCombobox.java
AddOn - Context Object Locator¶
col-vaadin This addon allows to store contextual information in the component hierarchy (e.g. a property containing the id of a selected entity).
Design patterns¶
For a general overview on how to develop with Vaadin, you can refer to the online version of the Book Of Vaadin Some of the important aspects are listed here.
Creating a server-side UI¶
Normally, you need to:
- extend the UI class
- build an initial UI from components
- define event listeners to implement the UI logic
Optionally, you can also:
- set a custom theme for the UI, for a harmonized look and feel it is however recommended to use the same theme for all UIs in cdm-vaadin
- bind components to data
- bind components to resources

Model-View-Presenter (MVP) Pattern¶
The recommended approach of implementing and wiring everything is the Model-View-Presenter (MVP) Pattern
The principle idea of pattern is described in section 11.10.2 of the Book of Vaadin. An example of the pattern in the project is the 'eu.etaxonomy.cdm.vaadin.view.AuthenticationView' class.

The spring-mvp pattern tries to decouple code and to create a structure so it is clear where to find the layout
and the logic of a application:
- The model (known as Bean, ValueObject(VO) etc.) contains the data to show in the application. In the above example the calculator class is the model class.
- The view contains only the layout.
- The presenter contains the logic for the layout.
The example given in the book of vaadin however is quite simple and misses covering important aspects of complex applications. For complex applications with modular nestable ui components a more sophisticated implementation of the pattern is required.
The blow UML like class diagram shows a implementation which follows in the basic idea the devday-spring example given at the Vaadin Dev Day 2016.
IMPORTANT
There are recet essential changes in the implementation of the MVP pattern which are not documented here. Please refer to the following list of tickets and commits:
- https://dev.e-taxonomy.eu/redmine/issues/6673 - PopupViewFactory
Further implementations of the MVP pattern¶
In the following the summary of the research on different implementations of the MVP pattern in vaadin applications is preserved as a reference:
Vaadin addons implementing the MVP pattern:
The spring-mvp-vaadin-addon has not yet converted to Vaadin 7 but provides valuable insight into building complex applications by implementing the MVP pattern with Spring. It introduces a central event dispatcher mechanism. Scoped event dispatchers are providing a solid infrastructure for an event based communication between the views and providers. There is a quite extensive handbook on this project https://flexguse.files.wordpress.com/2013/02/manual.pdf . The project is abandoned since 2013!
The Vaadin4Spring Extensions and Addons project is to be considered an add-on for the official Spring add-on. It provides two community contributed add-ons for implementing MVP:
- MVP by Chris Phillipson
- Simple MVP by Nicolas Frankel
Further mvp implementations:
The shortcoming of the vaadin calculator example initially publishe in the vaadin blog has also been discussed in the comments of the blo model-view-presenter-pattern-with-vaadin. In the according discussion thread rajeeshk comes up with a more elaborated appoach of a MVP framework example implementation which is available at github
rajeeshk/mvpcalculator.
Stefan Reisner also addresses in his blog post VaadinSpring und das Model-View-Presenter-Pattern the question of how the dependency injection fits best into the MVP pattern. In the second part VaadinSpring Model-View-Presenter-Pattern Teil 2/2 he addresses the modularization and re-usability which is based on inheritance. This approach is limited my the fact that a 'master' presenter always can inherit from one 'module'.
Another resource of information on MVP in general is http://www.gwtproject.org/articles/mvp-architecture.html
CDM Library Specific Development¶
This section lists the important CDM specific development issues to integrating Vaadin.
Managing Sessions¶
The strategies to solve the lazy loading problem and in more general to manage sessions properly include,
- Conversational Sessions : which essentially involves linking any UI which requires long running sessions to a 'eu.etaxonomy.cdm.vaadin.servlet.CdmVaadinConversationalServlet'. The servlet creates an instance of the ConversationHolder when a VaadinSession is initialized and binds it on every service call, ensuring that a single hibernate session is attached to a corresponding vaadin session.NOTE: One major issue with this strategy is the bug (#4528) which flushes the entire session even if a save / saveOrUpdate call is made on a single CDM entity. This implies that this strategy is safe to use only in 'session-save' UIs and not 'auto-save' UIs.
- OpenSessionInViewFilter : Servlet Filter that binds a Hibernate Session to the thread for the entire processing of the request. https://developer.jboss.org/wiki/OpenSessionInView
Exposing CDM Application Context¶
This issue relates to the problem that in the Vaadin framework it is not possible to autowire beans from the underlying application context as Vaadin prevents this possibility. To overcome this problem, a singleton helper class eu.etaxonomy.cdm.vaadin.util.CdmSpringContextHelper has been written to retrieve the beans given the bean name.
References and other goodies¶
- Vaadin Sampler - Component and feature reference application, with source code examples for all samples
- Vaadin Elements - Material design inspired UI components for building great web apps. For mobile and desktop.
- Icons - Searchable reference list of the Vaadin Icon set
- Valo Theme
- Valo Theme Demo - Component and style reference for the Valo theme. Preview of css styles for UI elements build into valo. Allow to quickly try out the different valo design themes. The source code for the demo is in https://github.com/vaadin/framework/tree/master/uitest/src/main/java/com/vaadin/tests/themes/valo
- Valo API Doc
- Valo SASS Examples SASS styles for the various valo subthemes Dark, Facebook, ...
- ValoTheme.class: Valo Component Styles to make them smaller, bigger, and so forth are defined in the ValoTheme class.
- Valo in the git repository
- Vaadin Designer
- Please also check the Webinars linked below
- Templates
- Webinars and Examples
- Video walk-through of creating an email client application, and the according code repository with documentation https://github.com/vaadin/designer-tutorials/tree/master/emailclient-tutorial
- Vaadin DevDay 2016 - Creating Vaadin UIs without coding, in plain HTML or in WYSIWYG the according soure code is here https://github.com/peterl1084/devday2016
- Vaadin DevDay 2016 - Supporting mobile, desktop and tablet by building impressive layout systems - the according soure code is here https://github.com/peterl1084/devday2016
- No video found so far - VaadinSpring based example project with MVP integration - the according soure code is here https://github.com/peterl1084/devday-spring
- https://vaadin.com/full-stack-starter : : Bakery App Starter for Vaadin Framework 8 and Spring. It is a reference implementation of a business grade full stack application built by the Vaadin Experts.
Performance¶
- https://vaadin.com/wiki/-/wiki/Main/Optimizing%20Sluggish%20UI
- https://dev.vaadin.com/wiki/Vaadin7/Features/LayoutPerformance
Miscellaneous Notes¶
- Currently the Server Push functionality of Vaadin has been disabled (by commenting out the relevant section in the pom file)
Conventions & Policies¶
Vaadin Security¶
Updated by Andreas Kohlbecker almost 7 years ago · 115 revisions